Small cell technology will play an integral role in the deployment of 5G networks. While macro cell deployments have rolled out to support consumer use cases, small cells will be deployed to support use cases for entertainment complexes, manufacturing facilities, healthcare organizations, and other enterprises. A recent study estimates that there will be 1.56 million private 5G small cells deployed by 2027, with the majority of deployments coming from enterprises.
But what is a 5G small cell and how can enterprises use them to support new use cases and ensure coverage and capacity where they need it most?
Here is a brief introduction to small cell technology and its potential applications to ensure interested enterprises leverage the timely opportunity to develop a strategy for accelerated deployment.
What is Small Cell Technology?
A small cell is a miniature wireless network base station with a low radio frequency power output and range. These nodes utilize radio equipment to receive and transmit data to smaller areas using low-, mid-, and high-band spectrum. Small cells deployed in 5G networks receive their connection from traditional cell towers before transmitting data from one cell to another in a relay, ensuring signals carry over large distances.
The small antennas are highly directional and leverage a technique called beamforming to direct coverage to specific areas around the site. Small cells require a power source and backhaul - fiber, wired, or microwave - to connect with 5G networks.
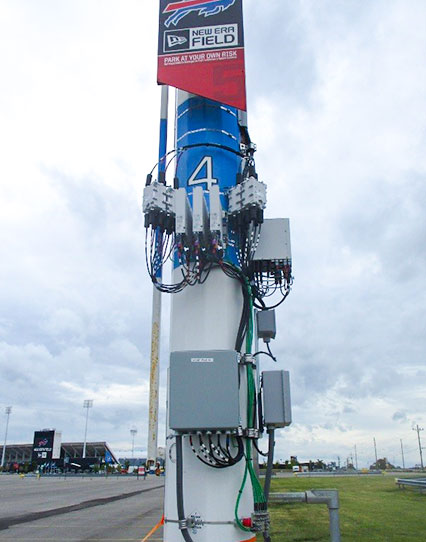
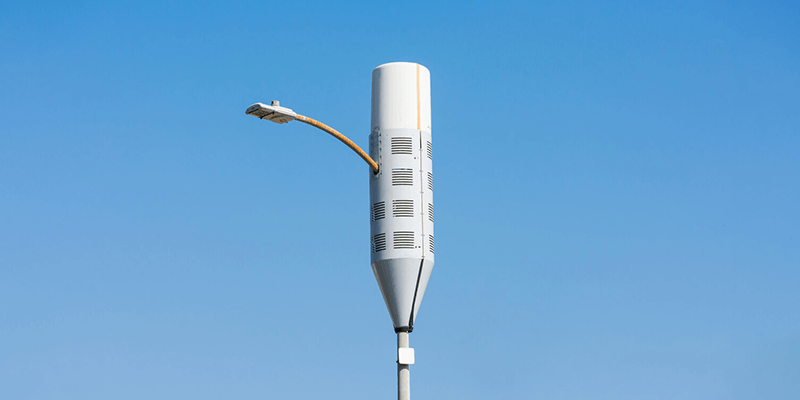
As the name suggests, small cells are relatively small in size as they don’t require much power and can be deployed for indoor or outdoor use in a licensed, shared, or unlicensed spectrum. Due to their size, they are easy to conceal and camouflage to blend with the natural environment. Base stations can be mounted on walls for indoor applications and placed on streetlights and utility poles for outdoor applications. Compared to large conventional cell towers, small cells are quick to install and are more affordable.
Small cell networks (SCNs) will play a key role in 5G infrastructure as the technology is crucial for network densification and ensuring superior coverage and signal penetration. In the 5G era, cell towers will be restricted to lower-level frequencies. SCNs will be used to support high-frequency millimeter wave transmissions and to complement the macro network by filling coverage gaps and adding targeted capacity.
What are the Different Types of 5G Small Cells?
Businesses need to be aware of the different types of 5G small cells as they have different coverage limits, power levels, and use cases. Compared to previous generations, small cells in 5G networks will be deployed in a wider range of scenarios with varied architectures.
Here are the three main types of small cells.
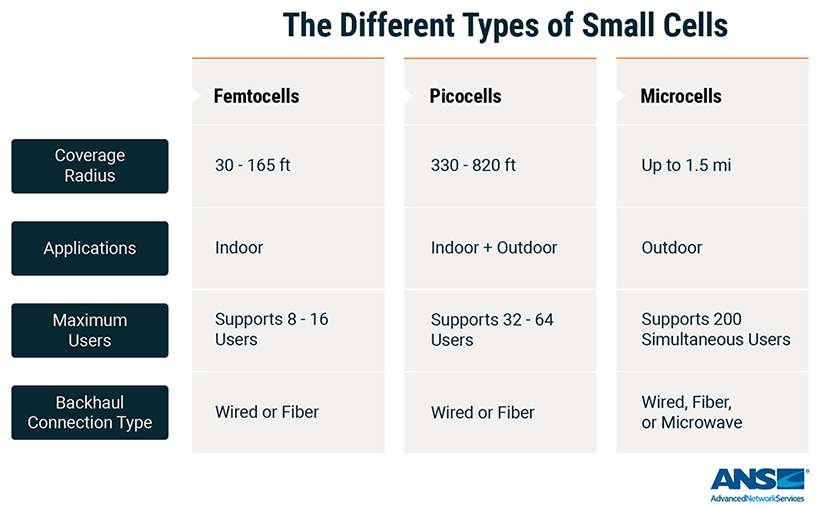
Femtocells - Used primarily as a low-cost solution to enhancing in-building coverage. Femtocells have a coverage range of 30-165 feet, support 8-16 users, and use a wired or fiber backhaul connection.
Picocells - Used to provide extended indoor and outdoor coverage for small enterprises such as higher education, offices, hospitals, and shopping complexes. Picocells cover 330-820 feet, support 32-64 users, and use a wired or fiber backhaul connection.
Microcells - Used to provide coverage to a targeted area such as hotels, malls, and unique spaces within transportation hubs. Microcells cover up to 1.5 miles, support 200 simultaneous users, and use a wired, fiber, or microwave backhaul connection. Microcells are more expensive than femtocells and picocells.
What are Potential Use Cases for 5G Small Cells?
From urban densification to extending private networks within enterprises, SCNs have many potential applications as they are ideal for use in places where cell towers can’t reach. They provide businesses an opportunity to harness the power of a 5G network with customization and precision for indoor and outdoor environments.
Here are several use cases to provide businesses a window into how they can benefit from 5G small cell deployment.
Commercial Facilities
Enterprises and commercial facilities like business parks, waterfront developments, office buildings, apartment complexes, and shopping malls can rely on SCNs to deliver reliable and secure in-building cellular connectivity for voice and data. When commercial facilities deploy their own 5G SCN, they can keep their data readily accessible and on-premise, ensuring a higher degree of security. In terms of cost, SCNs are a cost-effective workaround to 5G deployment, allowing businesses to forgo the need to build expensive macro sites.
Entertainment Complexes and Venues
Large venues have a host of connectivity challenges as they regularly experience significant demand peaks for a short period of time. If an entertainment complex needs more capacity as network demand grows, they can pinpoint where coverage is needed and then deploy additional nodes strategically to provide improved targeted coverage.
Industrial
5G SCNs will help enable Industry 4.0 capabilities. Industry 4.0 refers to the 4th industrial revolution which focuses heavily on automation, interconnectivity, machine learning, and real-time data. Manufacturing facilities with 5G capabilities have the capacity and latency requirements to support use cases including real-time asset tracking, robotic factories, autonomous guided vehicles, and more.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry can deploy a SCN to alleviate several major pain points including secure access to patient records and coverage for isolated indoor areas. Small cell-supported networks are secure and reliable, making them ideal for organizations that handle highly sensitive data.
Get 5G-Ready with a Reliable Small Cell Solution
Small cells promise a cost-effective solution for filling coverage gaps, increasing bandwidth, and getting networks ready for 5G without the need to build more expensive macro sites. Business owners and facility managers that understand the underlying technology and the potential use cases of 5G small cells are better positioned to partner with a premier integrator for rapid deployment.
As the importance of SCNs continues to become more apparent, businesses need to proactively assess emerging deployment opportunities and develop a strategy for implementation to position their organization for the future of communications technology.